Our Departments &
Equipments
Biochemistry
Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems
Biochemistry focuses on processes happening at a molecular level. It focuses on what’s happening inside our cells, studying components like proteins, lipids and organelles. It also looks at how cells communicate with each other, for example during growth or fighting illness.


Immunology
Immunology is the study of the immune system and is a very important branch of the medical and biological sciences. The immune system protects us from infection through various lines of defence. If the immune system is not functioning as it should, it can result in disease, such as autoimmunity, allergy and cancer. It is also now becoming clear that immune responses contribute to the development of many common disorders not traditionally viewed as immunologic, including metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s.
Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi and protozoa. This discipline includes fundamental research on the biochemistry, physiology, cell biology, ecology, evolution and clinical aspects of microorganisms, including the host response to these agents.


Hematology
Hematology, is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma.The laboratory work that goes into the study of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist.

Histopathology
Histopathology is the diagnosis and study of diseases of the tissues, and involves examining tissues and/or cells under a microscope. Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay.
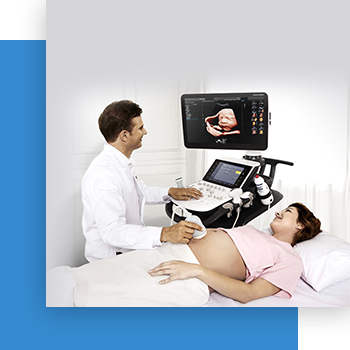
Radiology
Radiology is a branch of medicine that uses imaging technology to diagnose and treat disease. Radiology may be divided into two different areas, diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology.Diagnostic radiology refers to the field of medicine that uses non-invasive imaging scans to diagnose a patient. The tests and equipment used sometimes involves low doses of radiation to create highly detailed images of an area.
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum.[1] Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism),[2] against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease).





